When it comes to securing a conventional loan, one key factor that can make or break the approval process is the Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio. For many first-time homebuyers and real estate investors, understanding LTV ratios is critical to obtaining favorable loan terms and ultimately achieving financial goals. LTV ratios directly impact the amount a borrower can qualify for, the interest rate they’ll receive, and whether they’ll need to pay for additional mortgage insurance. In this article, we’ll explore how LTV ratios work, what borrowers need to know about down payments, and how they can improve their chances of securing the best loan terms.
What is Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio?
At its core, the Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio is a measure used by lenders to assess risk when offering a mortgage. It represents the percentage of the loan amount compared to the appraised value of the property. The higher the LTV ratio, the more risk the lender is taking on, as a larger portion of the home’s value is being financed by the loan.
How is LTV Calculated?
To calculate the LTV ratio, lenders use the following formula:

For example, if a borrower is looking to purchase a home worth $300,000 and plans to make a down payment of $60,000, they would need a loan of $240,000. In this case, the LTV ratio would be:
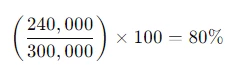
An 80% LTV means that the borrower is financing 80% of the property’s value, while the remaining 20% is covered by their down payment.
Why LTV is Important in Conventional Loan Approval
LTV ratios play a crucial role in the approval process because they give lenders a clear understanding of the level of risk they are taking on. Generally, the lower the LTV ratio, the more comfortable lenders are with approving the loan, often resulting in better loan terms for the borrower.
Lower LTV = Higher Approval Chances
A lower LTV ratio indicates that the borrower is contributing more upfront in the form of a down payment, reducing the lender’s risk. Borrowers with lower LTVs often receive more favorable loan terms, such as lower interest rates, reduced fees, and the possibility of avoiding Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI). Conversely, a higher LTV ratio may lead to higher interest rates and the requirement of PMI to protect the lender against the risk of default.
Higher LTV = More Risk
Lenders may be more cautious when considering loans with higher LTV ratios (typically above 80%). Borrowers with high LTVs are more likely to be required to purchase PMI, which adds an additional cost to their monthly payments. This is particularly important for first-time homebuyers who may have limited resources for a down payment.
The Relationship Between LTV and Down Payment
The down payment a borrower makes directly affects their LTV ratio. In general, the larger the down payment, the lower the LTV ratio, and the better the loan terms a borrower can expect.
Typical Down Payment Percentages
For conventional loans, borrowers are typically required to make a down payment of at least 20% to avoid paying PMI. However, many lenders offer programs that allow down payments as low as 3% for qualified borrowers, though this would result in a higher LTV ratio and the addition of PMI until the LTV reaches 80%.
Example of LTV Changes with Different Down Payments
If a borrower purchases a $300,000 home with different down payments:
- 20% down payment: $60,000 down, $240,000 loan = 80% LTV
- 10% down payment: $30,000 down, $270,000 loan = 90% LTV
- 3% down payment: $9,000 down, $291,000 loan = 97% LTV
The higher the LTV, the more expensive the loan becomes due to higher interest rates and PMI costs. Therefore, it’s important for borrowers to aim for a lower LTV whenever possible.
Improving Your Chances for Loan Approval with LTV
There are several strategies borrowers can use to improve their LTV ratio and increase their chances of securing a conventional loan.
Save for a Larger Down Payment
One of the most effective ways to reduce your LTV is to save for a larger down payment. By putting more money down upfront, you can lower your LTV ratio and improve your loan approval odds while also reducing the overall cost of the mortgage.
Purchase a More Affordable Home
If saving for a larger down payment is not feasible, consider purchasing a home that is below your maximum budget. A lower loan amount will reduce the LTV and make it easier to meet lender requirements.
Pay Down Existing Debts
Lenders also look at your overall financial picture, including debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, when determining loan eligibility. By reducing your existing debt, you can improve your creditworthiness and potentially secure better loan terms.
Conclusion
Understanding Loan-to-Value ratios is a critical component of the conventional loan approval process. Borrowers who have a clear grasp of how LTV ratios work and how they affect loan terms can better position themselves for approval and more favorable mortgage conditions. Whether it’s by saving for a larger down payment, reducing existing debt, or choosing a home within budget, taking steps to lower LTV can save money in the long run.
For those who need guidance, working with a trusted mortgage lender like A&D Mortgage can make the process smoother and increase the chances of success in securing a conventional loan.
FAQ
What is a good Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio for conventional loans?
An LTV ratio of 80% or lower is generally considered good for conventional loans. Borrowers with LTVs below 80% are often able to avoid PMI and may receive better interest rates.
How can I reduce my LTV ratio before applying for a loan?
To reduce your LTV ratio, you can save for a larger down payment, consider purchasing a more affordable home, or pay down existing debts to improve your overall financial profile.
What is the relationship between LTV and PMI (Private Mortgage Insurance)?
PMI is typically required for conventional loans with an LTV ratio above 80%. Borrowers can avoid PMI by making a larger down payment or refinancing once their LTV drops below 80%.
Does a higher down payment always lead to better loan terms?
Generally, a higher down payment results in a lower LTV ratio, which often leads to better loan terms such as lower interest rates, no PMI, and reduced fees.


