Blood pressure monitoring devices play a crucial role in managing hypertension and cardiovascular health. With a variety of options available in the market, selecting the most suitable device can be challenging. In this analysis, we compare two popular types of blood pressure monitors: manual sphygmomanometers and automated digital monitors, to help users make an informed decision.
Manual Sphygmomanometers:
Manual sphygmomanometers, also known as mercury or aneroid blood pressure monitors, have been a standard tool for blood pressure measurement for decades. They consist of an inflatable cuff, pressure gauge, and stethoscope.
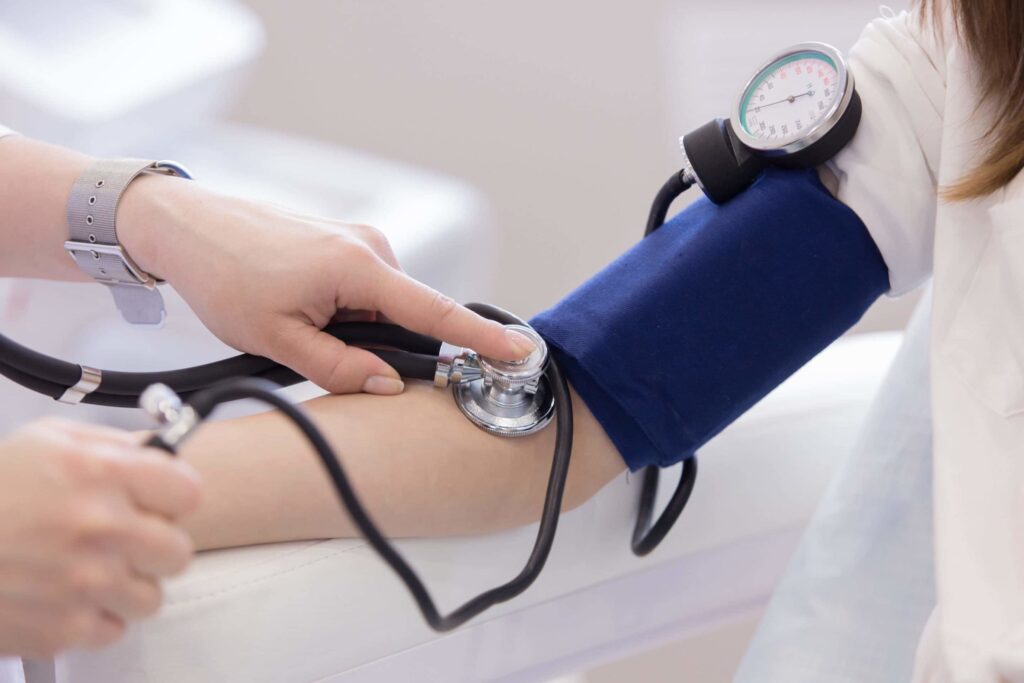
Here’s a closer look at the pros and cons:
Pros:
- Accuracy: Manual sphygmomanometers are considered the gold standard for accuracy, particularly in clinical settings, when used correctly.
- Durability: These devices are built to last, with minimal maintenance requirements and no dependence on batteries or electrical components.
- Affordability: Manual sphygmomanometers are often more affordable than automated digital monitors, making them accessible for home use.
Cons:
- Skill Required: Proper measurement with a manual sphygmomanometer requires training and skill to inflate the cuff, listen for Korotkoff sounds with the stethoscope, and interpret readings accurately.
- Subjectivity: Blood pressure readings may vary depending on the proficiency of the user, leading to potential inconsistencies.
- Time-Consuming: Manual measurements can be time-consuming, especially for individuals who require frequent monitoring or have mobility issues.
Automated Digital Monitors:
Automated digital blood pressure monitors have gained popularity for their ease of use and convenience. These devices typically feature an inflatable cuff and electronic display for blood pressure readings.
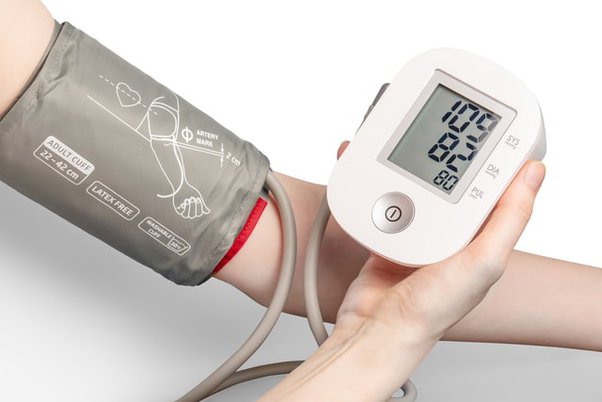
Let’s explore their pros and cons:
Pros:
- Ease of Use: Automated digital monitors are user-friendly, requiring minimal training or expertise for accurate readings.
- Convenience: These devices offer quick and convenient blood pressure measurements at the push of a button, ideal for home use.
- Memory and Data Storage: Many digital monitors come equipped with memory functions to store multiple readings over time, allowing users to track trends and share data with healthcare providers.
Cons:
- Accuracy Concerns: While modern digital monitors are generally accurate, they may be prone to inaccuracies due to factors such as cuff size, positioning, and user technique.
- Battery Dependence: Digital monitors rely on batteries or electrical power sources, requiring periodic replacement or charging.
- Cost: Automated digital monitors tend to be more expensive upfront compared to manual sphygmomanometers, although prices vary depending on features and brand.
Both manual sphygmomanometers and automated digital monitors have their merits and drawbacks. For individuals seeking unparalleled accuracy and reliability, particularly in clinical settings, manual sphygmomanometers remain the gold standard. However, for home use and convenience, automated digital monitors offer ease of use and data tracking capabilities.
Ultimately, the choice between manual and digital blood pressure monitors depends on factors such as individual preferences, budget, and the intended use of the device. It’s essential to consider these factors carefully and consult with healthcare professionals to determine the best option for accurate and effective blood pressure monitoring.

